Present State and Future Challenges of Android Based Voice Controlled Power Devices
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10862977Keywords:
mobile phone, voice controlled appliances, android, microcontrollerAbstract
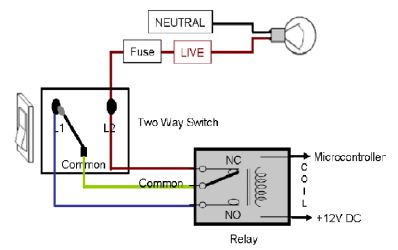
Automation of a modern person's surroundings enables him to work more comfortably and efficiently. Routine chores performed by an individual can now be automated, which is a major advancement. Nowadays, the majority of individuals spend their entire day glued to their smartphones and other smart gadgets. Therefore, by personifying the usage of the cell phone, several everyday domestic duties can be completed with the assistance of his friend. According to a market analysis of smart phones, new customers are choosing Android-powered devices. In layman's words, it has become a second name for a mobile phone. Voice Controlled Home Appliances (VCHA) automates an 8-bit Bluetooth-enabled microcontroller that regulates a variety of home appliances, including lights, fans, lamps, and many more, by means of an on/off relay. The device is designed for mobile phones running the Android operating system. This essay outlines an automated technique of home device control that could reduce the workload associated with utilizing the conventional switch method. In order to automate the system, Bluetooth—the most well-known and effective technology for short-range wireless communication—is used. With the ability to control up to 24 different appliances in any household setting, the VCHA system for Android users is a step in the right direction towards making duties easier
Downloads
References
M. Chan, D. Esteve, C. Escriba, & E. Campo. (2008). A review of smart homes—Present state and future challenges”, Computer methods and programs in biomedicine. Elsevier, 9I, 55-81.
J. Haartsen. (1998). BLUETOOTH—The universal radio interface for ad hoc, wireless connectivity. Ericsson Review, 3, 110-117.
http://www.android.com/about/.
R. Llamas, R Reith, & M. Shiere. (2013). Apple cedes market share in smartphone operating system market as android surges and windows phone gains. Available at: http://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS24257413.
N. Sriskanthan, F. Tan, & A. Karande. (2002). Bluetooth based voice controlled home appliances. Microprocessors and Microsystems, Elsevier, 26, 281289.
S. Panth, & M. Jivani. (2013). Designing voice controlled home appliances(VCHA) using java me for mobile phone. International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering, 2(02), 798-807.
S. Panth, & M. Jivani. (2013). Device control in an ad-hoc network environment by using mosync for multiple platform mobile application development. International Journal of Computer Science & Engineering Technology, 4(08), 1145-1152.
http://www.ucmicrosys.com/products/ic-programmers/ucflash.html.
http://www.atmel.com/images/doc0265.pdf.
A.Göransson, & D.C.Ruiz. (2013). Android open accessory programming with arduino.
Dr. O. P. Meena. (2023). Wireless communication engineering experiments using MATLAB. Lucknow, India: Vandana Publications.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
ARK
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Dr. Shubham Namdesjwar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Research Articles in 'Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research' are Open Access articles published under the Creative Commons CC BY License Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. This license allows you to share – copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format. Adapt – remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.










