Alkali Interaction with Expansive and Non Expansive Soils
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15107823Keywords:
alkali, soil, propertiesAbstract
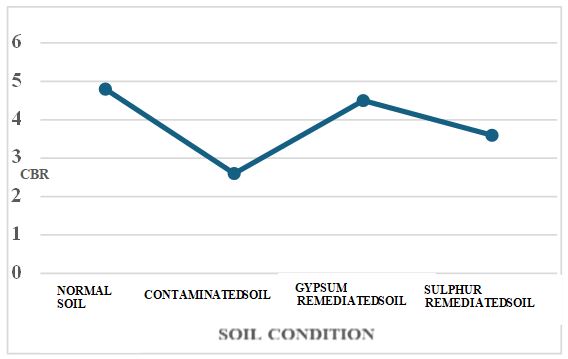
This research examines the interaction of alkali contaminants with both expansive and non-expansive soils, specifically black cotton soil and red soil, while assessing the effectiveness of sulphur and gypsum in restoring soil pH for geotechnical stability. Alkaline contamination, commonly caused by industrial effluents, construction activities, and agricultural practices, alters soil behavior by influencing its strength, swelling-shrinkage properties, and overall suitability for construction and infrastructure development. Laboratory experiments are conducted to evaluate the impact of alkalinity on key soil properties, including Atterberg limits, swelling potential, shear strength, permeability, and consolidation characteristics.
Expansive soils, such as black cotton soil, exhibit significant volume changes with moisture fluctuations, whereas non-expansive soils like red soil respond differently to alkali exposure. The presence of alkali contaminants can lead to reduced cohesion, increased dispersibility, and diminished bearing capacity, which pose risks to foundations, pavements, and embankments. This study investigates the potential of sulphur and gypsum as chemical stabilizers to counteract the negative effects of alkalinity. Controlled soil treatment trials are conducted to systematically assess variations in soil pH, structural integrity, and overall engineering performance.
The results offer valuable insights into the geotechnical consequences of alkaline contamination and the effectiveness of remediation techniques in stabilizing affected soils. By addressing the challenges posed by contaminated soils in civil engineering applications, this research contributes to sustainable ground improvement strategies, enhancing the durability and safety of infrastructure projects in impacted areas.
Downloads
References
Mechanical and microstructural characteristics of undisturbed lateritic soil subjected to alkali contamination. Original Paper Published: 29 November 2023 Volume 82, Article Number 469.
Atul Soni, & Deepak Varshney. (2021). Experimental study of the effect of alkali contamination on geo-mechanical properties of the soil. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1116 012173.
Dima A Malkawi, Samer R Rabab’ah, Malak M AlSyouf, & Hussein Aldeeky. (2023). Utilizing expansive soil treated with phospho gypsum and lime in pavement construction. Results in Engineering, 19, 101256.
Peng Zhang, Yulin Dong, Yujie Guo, Chengcong Wang, Guodong Wang, Zijun Ma, Wei Zhou, Dan Zhang, Zhibin Ren, & Wenjie Wang Catena. (2023). Urban forest soil is becoming alkaline under rapid urbanization: A case study of Changchun, northeast China.
Qi Jiang, Yongmei He, Yonglin Wu, Bo Dian, Jilai Zhang, Tianguo Li, Ming Jiang. (2022). Solidification/stabilization of soil heavy metals by alkaline industrial wastes: A critical review. Environmental Pollution, 312, 120094.
Chavali Rama, Vara Prasad, P. Hari Prasad Reddy, V. Ramana Murthy, & P.V. Sivapullaiah. Swelling characteristics of soils subjected to acid contamination Author links open overlay panel.
Yashar Alibeiki, Mahmoud Hassanlourad, & Amirhossein Ghasemipanah. (2022). Effect of acidic and alkaline pore fluid on the mechanical properties of fine-grained soil. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 81(12), 512.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
ARK
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neethu John, Mohamed Nihal N, Niveditha KS, Renil Das, Ridhick Prakash J

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Research Articles in 'Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research' are Open Access articles published under the Creative Commons CC BY License Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. This license allows you to share – copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format. Adapt – remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.










