Crossbreed Cloud
Using a combination of private and public clouds, hybrid cloud computing allows businesses to take advantage of the best of both worlds by utilising the best of both worlds for some of their most critical functions while also utilising the public cloud for less critical ones.
Community Cloud
All of the participating organisations or a third-party managed service provider govern, manage and secure a community cloud infrastructure. Each of these organisations is based on the same technology and has a similar set of issues to address.
DELIVERY MODELS OF CLOUD COMPUTING
Three main cloud computing delivery prototypes are Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), the Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
The Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is the most basic form of cloud computing. Servers, storage, networking equipment (such as routers), and operating systems are all available as a service through Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Instead of purchasing these resources, you can simply call up a cloud service provider and have them delivered when you need them when you need them. This helps organisations save money.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
The Platform-as-a-Service occupies the middle ground. Platform-as-a-Service facilitates the rapid and efficient creation of software applications by providing a set of development tools and services. There are also applications-related services that can be hired.
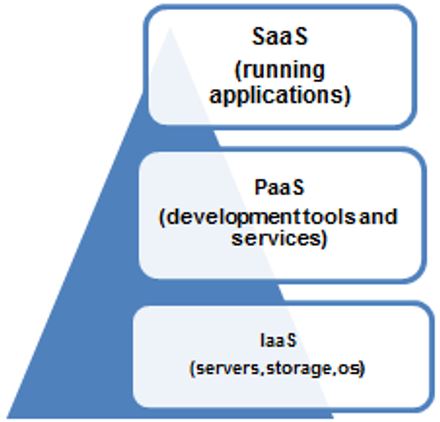
Figure 3: Delivery Models of Cloud Computing
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
The Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) occupies the highest position. Software and its functions can be accessed via web-based services such as email and Google docs in this model. Organizations can get into services at a fraction of the cost of purchasing licenced applications thanks to Software-as-a-Service. After the result of the software being hosted remotely, users are spared the costs and hassles of purchasing and setting up additional hardware.
Cloud Computing Security Issues
Cloud computing safety and privacy are major concerns. Many people find it intimidating to store their data on someone else's servers, run their programmes on someone else's CPUs, or create software using someone else's tools.
Operating systems, networks and databases are among the many systems that make up cloud computing. It also includes features such as load balancing and currency control. Although there are numerous security concerns, we will only address a few of them in this article.
Information Confidentiality Issue
Data belonging to multiple customers may be stored on the same server in a cloud computing platform (hardware, operating system, and storage). When one customer's personal information is accidentally shared with another, there is a risk of information leakage.
Hyperjacking
Cybercriminals are devoting significant resources to finding ways to breach the cloud. It is theoretically possible for hackers to take over vast amounts of data by "hyperjacking" large cloud servers, which store data from a large number of different companies.
Data Availability Issue
When storing data in a third-party location, the data owner runs the risk of a service provider's system failing. Because it is dependant on a single service provider, the data will be unavailable if the cloud goes down. The objective of cloud computing is to deliver a variety of on-demand services.


 ©
©